
Image Source: What Age You Should Start Teaching Your Children About Investing? | Trader
Investing in the stock market is often seen as a pursuit reserved only for adults.
But what about kids? Can they also take part in controlling their financial future?
To answer this question, today we’re going to explore the possibility and opportunities of kids not just having a savings account but actually investing money into the stock market.
The idea of children learning about stocks may seem a bit out of the ordinary, but it presents an excellent opportunity for them to learn about financial responsibility and the value of money. This isn’t just about making money; it’s about gaining vital life skills like making smart financial decisions and understanding risk.
Our goal today is to simplify the complexities of the stock market for young minds. We will cover everything from legal aspects to the potential benefits and risks involved. Whether you are a parent considering this educational opportunity for your child or a younger person eager to learn about stocks, this guide is designed to give you everything you’ll need to start investing today.
Understanding the Age Requirements for Young Investors

Image Source: How Old Do You Have to Be to Invest? | Acorns
When it comes to investing in stocks, one of the first questions that comes to mind is: “How old do you have to be?” The answer is not as straightforward as one might think, as it varies depending on where you live.
In most countries, the legal age to independently open and manage a brokerage account is 18. This is the age when an individual is generally considered a legal adult, capable of making their own financial decisions. But this doesn’t mean that those under 18 are completely excluded from the stock market.
For younger investors who are keen to start early, there’s a common solution: custodial accounts. These accounts allow a parent or guardian to open and manage an investment account on behalf of a minor. While the adult holds the legal responsibility for the account, the assets within it belong to the child. This setup not only provides a legal pathway for minors to invest in stocks but also offers a hands-on educational experience under the guidance of an adult.
It’s important to note that these custodial accounts come with specific rules and regulations, which can vary based on the country or region you live in. For instance, in the United States, two popular types of custodial accounts are UGMA (Uniform Gifts to Minors Act) and UTMA (Uniform Transfers to Minors Act) accounts. These accounts have different implications for control and taxation, which should be carefully considered before opening one.
Parents and guardians play a crucial role in this process. It’s their responsibility to understand the legalities and implications of opening and managing a custodial account. They should also be aware that once the child reaches the age of maturity (18 in most cases), they will gain full control over the account and its assets.
Investment Account Options for Kids
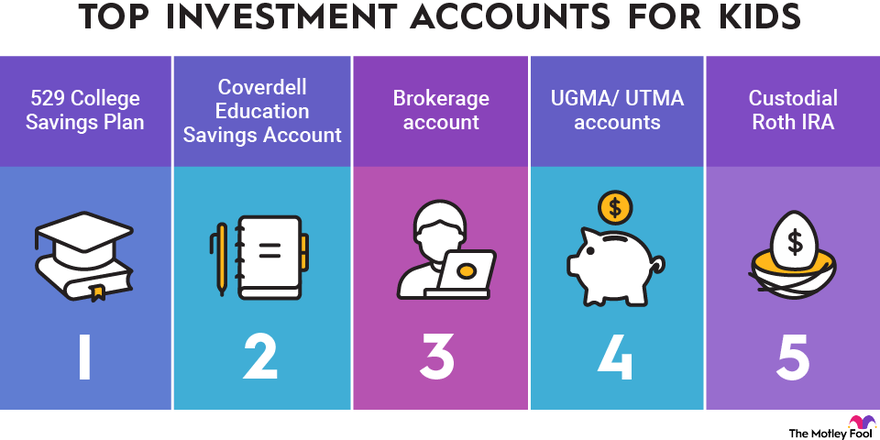
Image Source: Best Investment Accounts for Kids in 2024 | The Motley Fool
For young investors and their parents, understanding the different types of accounts available for investing in stocks is crucial. Obviously, each account has its own features, benefits, and drawbacks, and the type of account that will work best for you will depend on your specific financial situation.
Below, we’ve highlighted the most popular kinds of accounts that kids will be able to take over when they get older.
529 College Savings Plans
A 529 plan is primarily an education savings plan, helping families set aside funds for future college costs. Although it’s not a traditional stock investment account, it allows for investment in stock-based assets. The key advantage of a 529 plan is its tax benefits, with earnings growing tax-free if used for qualified educational expenses. This makes it a suitable choice for parents prioritizing educational savings, albeit with some limitations on investment control.
Custodial Brokerage Account (UGMA/UTMA)
As mentioned above, custodial brokerage accounts allow parents to invest in individual stocks or various other investment funds on behalf of their children. The assets in these accounts are owned by the child but managed by the parent until the child reaches adulthood.
Custodial accounts stand out for their flexibility in fund usage, not being restricted solely to educational expenses. They serve as a practical tool for teaching kids about investing, offering broad exposure to various investment types. Additionally, the types of investments allowed in these accounts are not limited. From mutual funds, stocks, and exchange traded funds to other kinds of assets, parents and kids may choose a wide variety of different investments.
Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) for Minors
For minors with earned income, an IRA (either Traditional or Roth) can be a great introduction to long-term investing. These accounts are primarily intended for retirement savings, but they offer a unique way for young earners to start investing early.
The contribution to these accounts is limited to the lesser of the minor’s annual earned income or the standard yearly IRA contribution limit. These accounts are an excellent way to instill the habit of saving and investing from a young age, with a focus on long-term growth rather than immediate returns.
Teen-owned Brokerage Accounts
Some financial institutions have tailored brokerage accounts for teenagers (usually aged between 13 and 17). These accounts often transition into standard adult accounts when appropriate. They provide an opportunity for teenagers to make investment decisions under the watchful eye of their parents.
Trust Funds
Trust funds are a more complex option involving a legal arrangement where assets are held and managed by a trustee for the child’s benefit. They can be specifically set up for investment purposes and offer a high degree of control over when and how the child can access the funds. Trust funds are often used for larger estates or when specific conditions for fund distributions are desired.
Education Savings Accounts (ESA)
ESAs (Education Savings Accounts) offer another avenue for saving for educational expenses. Like 529 plans, they provide tax-free growth and withdrawals for qualified expenses. However, they differ in their flexibility, allowing for spending on a broader range of educational costs, including elementary and secondary education. This makes them a great option for parents who anticipate diverse educational expenses.
Each of these account types brings its own set of rules, benefits, and limitations to the table. Parents and young investors should carefully weigh these factors against their financial goals and needs. Consulting a financial advisor to navigate these options can also be a wise step when trying to decide which type of account is best for you.
Benefits of Early Investing

Image Source: This Investing Strategy Has a 100% Success Rate, But It Comes With a Very Big Catch | The Motley Fool
Investing can be an extremely valuable skill to have early on in life. And in truth, even most adults struggle to manage their investment portfolio successfully.
This is the exact reason why encouraging kids to begin investing early on can be so powerful.
For our parent readers who want to know what exactly will come of having their kids play an active role in their investment decisions, below we’ve outlined the top benefits of kids investing early in life.
Compound Interest: The Power of Time
One of the most compelling reasons for early investment is the power of compound interest. This is the ability of an asset to generate a return, which is then reinvested to create its own return.
In simple terms, it’s earning interest on interest, and the earlier one starts, the more significant the compounding effect will be. For young investors, this means that even small investments can grow substantially over time, setting the foundation for substantial financial growth and security in the future.
Developing Financial Literacy and Responsibility
Early exposure to the stock market will instill robust financial literacy from a young age. Understanding how the stock market works, the value of money, and the concept of investment risks and returns are crucial life skills. This knowledge empowers young individuals to make better financial decisions, including when to sell stocks, adjust allocations, and gain a broad overview of the personal finance decisions they will have to make when they’re older.
Learning the Discipline of Saving and Investing
Investing in stocks teaches the importance of saving and investing rather than just spending. It instills a sense of discipline and planning in financial matters. Young investors learn to set financial goals and understand the importance of patience and consistency in achieving these goals. This discipline, once developed early in life, should carry over into other aspects of a kid’s personal and professional life.
Embracing Risk Management Skills
Investing in the stock market exposes young investors to the concept of risk. Learning to manage and mitigate risk is an essential skill not just in finance but in life decisions as well. Early investing experiences, especially in a controlled environment with parental guidance, will provide untold value in effectively assessing and handling risk.
Long-Term Financial Confidence and Independence
Early investors are likely to grow into adults who are confident in managing their finances. This confidence, rooted in years of learning and experience, paves the way for financial independence. They are more likely to be proactive in planning for life events, such as higher education, homeownership, or retirement, making them well-equipped to face financial challenges and opportunities.
In summary, the benefits of opening an account for your child early extend far beyond the potential financial gains. It’s about laying a foundation for financial wisdom, responsibility, and independence.
For parents, this is an opportunity to set their children on a path to a secure and successful financial future. And for young investors, it’s a chance to grow their financial acumen and confidence and learn about the exciting new world of stocks!
Educational Resources for Young Investors

Image Source: 6 Ways to Get Kids Excited About Investing | NerdWallet
For younger investors eager to learn about the stock market, specific books, online courses, and investment simulations can provide valuable experience.
Below, we’ve compiled some resources for new investors that should help them learn about important basics when investing, like how to buy a stock, what to look for when investing, risk management concepts, and how the stock market works.
Books and Literature
- For Younger Children: Finance 101 for Kids by Walter Andal provides an excellent introduction to basic money concepts, including stocks. It’s engaging and easy to understand for children.
- For Teenagers: The Motley Fool Investment Guide for Teens by David and Tom Gardner offers a more in-depth look into investing, tailored to a teenage audience. It covers everything from setting up an investment account to picking stocks.
- Advanced Reading: The Young Investor: Projects and Activities for Making Your Money Grow by Katherine R. Bateman is ideal for teenagers who already have a basic understanding of stocks and want to dive deeper. It includes practical activities and projects to apply learning.
Online Courses and Workshops
- Beginner Courses: Websites like Udemy and Coursera offer beginner-level courses in stock market basics, suitable for young learners. For example, “Investing Basics for Kids” on Udemy teaches the fundamentals in an easy-to-grasp manner.
- Intermediate to Advanced: For more advanced young investors, Khan Academy provides in-depth lessons on financial markets, investment strategies, and financial planning. Their courses are free and widely respected.
Investment Simulations and Games
- The Stock Market Game: This simulation game allows students to manage a virtual investment portfolio. It’s a popular tool in schools and provides a realistic experience of trading in the stock market.
- HowTheMarketWorks: This free website offers a realistic simulation of the stock market. Users can create custom contests for themselves and friends, making learning both competitive and fun.
- Wall Street Survivor: Combining both learning and playing, this platform offers courses and stock market games. It’s a great way to learn trading strategies while virtually investing in real-time market conditions.
These resources are designed to cater to varying levels of understanding and interest, ensuring that there’s something for every young investor. Books provide the foundational knowledge, online courses offer structured learning paths with expert guidance, and simulations bring the world of the stock market to life. Together, these resources should form a comprehensive toolkit for any young individual looking to understand and succeed in investing.
Parental Involvement and Guidance

Image Source: Tidy your room!’: a teenager’s guide to arguing with your parents | Young people | The Guardian
Empowering children to manage their own investment portfolios presents a unique opportunity to teach them about independence, the stock market, and risk management. However, this empowerment is most effective when there is a careful balance between allowing them to make their own decisions (and mistakes) and providing the necessary guidance and support when needed.
To emphasize this point, this section will discuss the benefits of encouraging kids to make their own investment decisions and inevitably learn from their mistakes as they progress in their investing experience.
Fostering Independence Through Controlled Risk
Allowing children to make their own investment decisions—within set boundaries—is crucial for their learning. Parents can establish a framework within which kids can make choices, such as selecting stocks from a pre-approved list or allocating a certain percentage of their portfolio to their own picks. This approach gives them a sense of control and ownership while also limiting potential risks.
Learning from Mistakes
One of the most valuable aspects of investing at a young age is the opportunity to learn from mistakes in a relatively low-stakes environment. Parents should resist the urge to step in at the first sign of a poor investment decision. Instead, use these moments as teaching opportunities to discuss what went wrong and how to make better-informed decisions in the future.
Providing Guidance When Needed
While it’s important for kids to have the freedom to explore and learn, parents should be ready to provide guidance when necessary. This might mean discussing the fundamentals of stock market investing, helping them understand the impact of economic events on their investments, or simply being there to answer questions and offer advice.
Adjusting the Level of Involvement
The level of parental involvement should evolve as the child grows and their understanding of investing deepens. Younger children may need more direct guidance, while teenagers might benefit from a more hands-off approach, with parents stepping in only when asked or when they see a teachable moment.
Encouraging Reflection and Learning
Parents should encourage their children to reflect on their investment decisions, both good and bad. This reflective process helps in developing critical thinking and a deeper understanding of investing strategies. Regular discussions about their portfolio’s performance, recent market trends, and future goals can be instrumental in this learning process.
The goal of parental involvement in a child’s investment journey is to find the right balance between guidance and independence. By providing a safe space for kids to make their own decisions, learn from their mistakes, and seek guidance when they need it, parents can help nurture a sense of responsibility, a deeper understanding of the stock market, and the confidence to make independent financial decisions in the future.
Conclusion
Introducing children to stock investing is a significant step in developing their financial independence and understanding. Guided by their parents, children will gain practical insights into the stock market, learn about risk management, and appreciate the role of money in everyday life.
This early engagement in managing investments is more than just an educational experience; it’s a foundation for a financially savvy future.
It prepares the next generation to navigate the complexities of finance with confidence, skill, and poise.
Disclosure/Disclaimer:
We are not brokers, investment, or financial advisers; you should not rely on the information herein as investment advice. If you are seeking personalized investment advice, please contact a qualified and registered broker, investment adviser, or financial adviser. You should not make any investment decisions based on our communications. Our stock profiles are intended to highlight certain companies for YOUR further investigation; they are NOT recommendations. The securities issued by the companies we profile should be considered high risk and, if you do invest, you may lose your entire investment. Please do your own research before investing, including reading the companies’ public filings, press releases, and risk disclosures. The company provided information in this profile, extracted from public filings, company websites, and other publicly available sources. We believe the sources and information are accurate and reliable but we cannot guarantee it. The commentary and opinions in this article are our own, so please do your own research.
Copyright © 2023 Edge Investments, All rights reserved.
