Image Source: Big Data Analytics | Utimaco
Big data refers to the large volumes of data—structured, unstructured, and semi-structured—generated every minute, from various sources like social media, business transactions, online interactions, and IoT devices.
The importance of big data isn’t just in its size but in its utility, or in other words, the true value of big data comes from the ability to process and analyze vast datasets to uncover patterns, trends, and insights that were previously inaccessible.
In today’s article, we will examine the top big data trends that are reshaping the industry as new technologies and priorities shift how companies use big data in the future.
Emerging Trends in the Big Data Industry
The big data industry is in a constant state of flux, driven by evolving technologies and shifting business needs.
Here, we’ll dive into the pivotal trends that are currently shaping big data today.
Trend #1: Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Image Source: How Big Data And Artificial Intelligence Work Together – Big Data Analytics News | Google
The fusion of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) with big data analytics is a trend that has been developing for many years, though with the recent advancements in AI models, this trend is set for renewed growth.
Below, we’ve broken down the key drivers of AI being integrated into big data:
Enhancing Data Processing Capabilities
AI and ML algorithms have revolutionized the way data is processed. By automating complex and time-consuming tasks, these technologies have drastically reduced the time needed for data processing. AI models can quickly analyze huge data sets, identify patterns, and extract important information, thereby assisting data scientists and businesses in finding important correlations within data sets.
AI Yields More Accurate Predictions
One of the most significant advantages of integrating AI and ML in big data analytics is the ability to make more accurate predictions.
ML algorithms, through their learning capabilities, continuously improve over time. They can analyze historical data, learn from trends, and make predictions about future outcomes with a high degree of accuracy. This predictive power is invaluable in many different sectors, as businesses look to find data driven ways to help make better strategic decisions.
Delivering Deeper Insights Across Various Domains
AI and ML’s ability to process and analyze big data goes beyond surface-level insights. These technologies can dive deeper into both structured and unstructured data, uncovering hidden patterns and subtle correlations that would be invisible to human analysts.
Transformative Impact on Industries
- Healthcare: In healthcare, AI and ML are being used for predictive diagnostics, personalized treatment plans, and drug discovery. By analyzing patient data and medical records, these technologies can predict disease outbreaks, identify potential health risks, and offer personalized treatment recommendations.
- Finance: The finance sector leverages AI and ML for risk assessment, fraud detection, and algorithmic trading. By analyzing market data and customer behavior, financial institutions can identify potential frauds, assess credit risks, and make real-time trading decisions.
- Retail: In retail, AI and ML contribute to enhancing customer experiences through personalized recommendations, inventory management, and trend analysis. Retailers are using customer data to predict buying patterns, manage stock levels, and create targeted marketing campaigns.
Challenges and Future Prospects
While the integration of AI and ML in big data analytics offers many benefits, it also presents challenges such as ethical considerations, data privacy concerns, and the need for skilled professionals to manage and interpret AI/ML outputs.
As we move forward, these technologies are expected to become even more sophisticated, with advances in areas like natural language processing, computer vision, and deep learning, meaning the integration of AI into big data processes is only just getting started.
Trend #2: Data Fabric: The New Reality in Data Integration
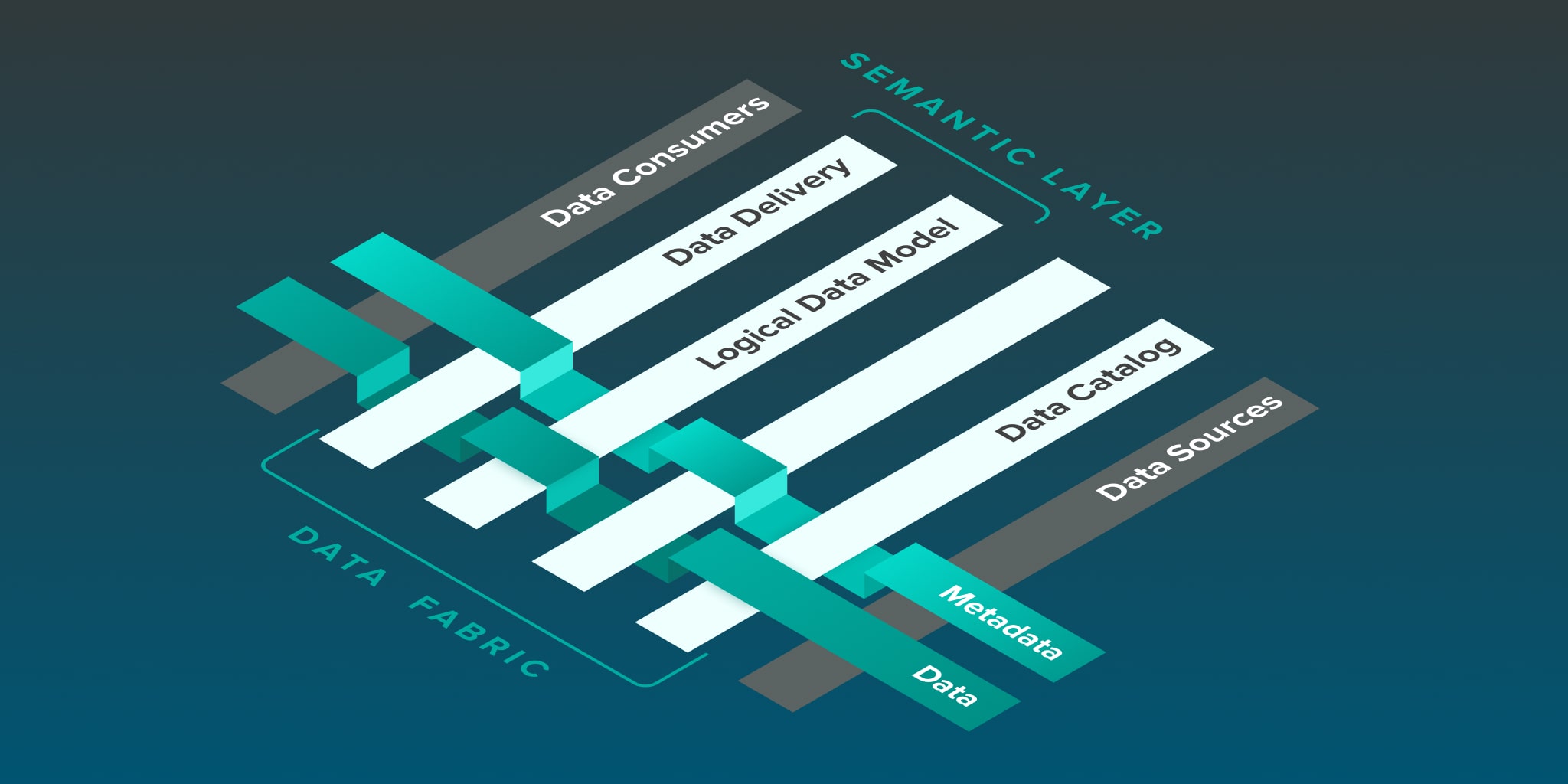
Image Source: What Is a Data Fabric? – Definition, Architecture & More | AtScale
Data fabric is quickly becoming a cornerstone trend in the big data management.
This innovative approach represents more than just a technology or process change; it’s an all encompassing architecture and set of data services designed to address the complexities of modern data environments.
Understanding Data Fabric Architecture
At its core, data fabric architecture is about creating a unified, integrated layer that brings together different data management processes. It encompasses various components such as data integration, data governance, and data security, all working in a single platform.
This architecture allows for the seamless connection of data sources across different environments, be it on-premises, cloud, or hybrid systems. The goal is to provide a consistent and controlled data management framework that can adapt to any data ecosystem.
Seamless Integration Across Diverse Environments
The reason why data fabric is becoming such an important trend is the ability for companies to perform their data collection through many different sources. Implementing a data fabric solution gives firms the ability to integrate data across diverse platforms and environments, including hybrid and multi-cloud systems.
This flexibility is crucial in today’s world, where data is spread across various locations and formats. Data fabric ensures that this dispersed data can be accessed and analyzed cohesively, providing a comprehensive view of a companies vast customer data set.
Agile Data Access, Management, and Governance
Data fabric also offers agile data access, enabling users to retrieve and analyze data quickly, regardless of its location. This agility is essential for organizations needing real-time data analysis and decision-making capability.
Moreover, data fabric streamlines data management and data storage, simplifying the complexities of handling large volumes of data from different sources. In terms of governance, data fabric provides a framework for data quality, privacy, and compliance, ensuring that data management adheres to regulatory standards and best practices.
In short, the rise of IoT, AI, and other technologies has led to an explosion in data volume, variety, and velocity. Managing this diverse and distributed data is an understated challenge for many organizations.
Data fabric solutions address these complexities by providing a unified platform that can handle various data types and sources. It enables organizations to break down data silos, facilitating better data sharing and collaboration.
Trend #3: Enhanced Focus on Data Privacy and Security

Image Source: Data Privacy vs. Data Security: Understanding the Difference and Overlap | Drata
As the digital world continues to be driven by massive volumes of data, the focus on privacy and security has become a criticized topic.
Consumers and governments continue to raise their concerns on data security, meaning the development of data privacy and security policies will undoubtably have a large impact on the industry moving forward.
Increasing Importance of Data Security
Organizations are increasingly aware of the risks associated with data breaches and cyber threats.
This awareness has led to a heightened focus on implementing advanced security measures, as well as evolving regulations that will have a large impact on how big data companies operate.
More specifically, below is a detailed list on how the increasing scrutiny on data security will effect the big data industry moving forward:
- Evolving Security Technologies: The big data industry will need to continuously evolve its security technologies to keep pace with emerging threats. Encryption, tokenization, and access controls will become necessities in the industry.
- Investment in Security Infrastructure: Companies handling big data will have to invest more in their security infrastructure. This includes not only software and hardware but also in training employees to recognize and respond to cyber threats effectively.
- Innovation in Security Solutions: The big data industry will likely drive innovation in security solutions, given its need to handle vast amounts of data securely. This could lead to new security products and services tailored to the specific needs of big data processing.
- Impact on Data Accessibility and Usability: While securing data is critical, overly stringent security measures could impede data accessibility and usability. Finding the right balance between security and ease of data use will be crucial moving forward.
- Collaboration and Information Sharing: Finally, there’s likely to be an increase in collaboration among big data companies, security solution providers, and regulatory bodies to share best practices, threat intelligence, and strategies to combat cyber threats effectively.
Future Challenges and Opportunities
As technology continues to evolve, so do the challenges surrounding data privacy and security. The rise of technologies like IoT, AI, and cloud computing introduces new vulnerabilities and complexities in data protection.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation in cybersecurity and privacy technologies.
The future will likely see continued advancements in security methodologies, as well as a greater emphasis on embedding privacy and security into the design of data systems and processes.
The Rise of Edge Computing in Data Analytics
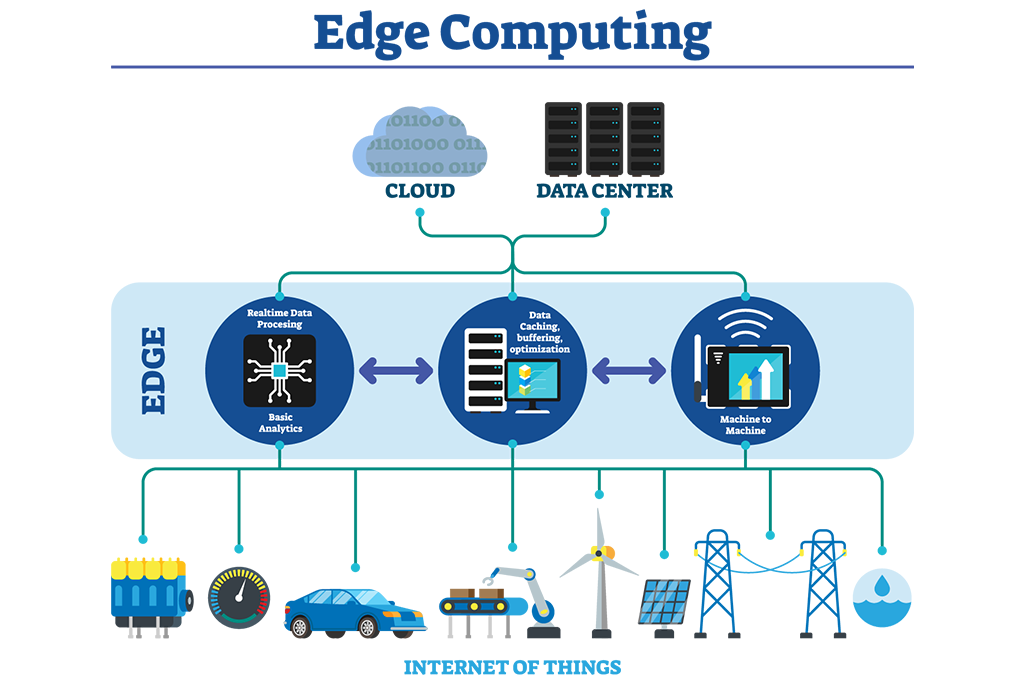
Image Source: Real-Life Use Cases for Edge Computing | IEEE Innovation at Work
Edge computing has emerged as a vital technology in predictive analytics, particularly gaining traction in applications where real-time data processing is critical.
This shift towards edge computing represents a significant evolution in how data is handled and analyzed, bringing computing power closer to the source of data generation.
Bringing Data Processing Closer to the Source
Traditionally, data generated by devices and sensors was sent back to centralized data centers or cloud platforms for processing by data engineers. This approach, while functional, often led to latency issues and high bandwidth usage, which is particularly problematic in real-time applications.
Edge computing addresses these challenges by bringing the data processing capabilities closer to where data is generated. By doing this, it dramatically reduces the time taken to process data, leading to quicker decision-making and action.
Reducing Latency and Conserving Bandwidth
One of the primary benefits of edge computing is the significant reduction in latency. Since data is processed locally, rather than being transmitted to a distant server, the response time is much quicker. This reduction in latency is crucial in applications like autonomous vehicles, where milliseconds can make a difference in safety-critical decisions.
Additionally, by processing data locally, edge computing reduces the bandwidth needed to transmit data to and from a central server, leading to more efficient use of network resources and faster business processes.
Transformative Impact on Various Sectors
- Autonomous Vehicles: In autonomous vehicles, edge computing enables real-time data processing, crucial for immediate decision-making on the road. Sensors in vehicles generate vast amounts of data that need to be processed instantaneously to ensure safe navigation and operation.
- Smart Cities: For smart city initiatives, edge computing facilitates the real-time analysis of data from various sources like traffic cameras, sensor-equipped infrastructure, and public service vehicles. This real-time processing capability is essential for managing city services efficiently, such as optimizing traffic flow and energy usage.
- Real-Time Health Monitoring Systems: In healthcare, edge computing plays a critical role in real-time health monitoring systems. Wearable devices and medical sensors can process data on the spot, providing immediate insights into a patient’s health status. This capability is particularly important for monitoring chronic conditions or for elderly care, where timely intervention can be life-saving.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While edge computing offers significant advantages, it also presents challenges, such as ensuring data security and privacy at the edge, managing the deployment and maintenance of edge devices, and integrating edge computing with existing IT infrastructure.
As the technology progresses, we can expect further advancements in edge computing capabilities, including better integration with cloud services, enhanced security features, and more sophisticated data analytics tools optimized for edge deployment.
This ongoing development will continue to expand the potential and applications of edge computing in various industries, making it a key component in the future of big data analytics.
Real-Time Analytics: Accelerating Decision-Making and Insights

Image Source: An In-Depth Guide to Real-Time Analytics | Striim
Along with the above trend of edge computing, real-time analytics is quickly becoming a critically important in big data, reshaping how organizations process and utilize data for decision-making.
This trend reflects the growing need for immediate insights and actions in a fast-paced digital world.
Instantaneous Data Processing and Analysis
The essence of real-time analytics lies in its ability to process and analyze data as it is generated, providing insights almost instantaneously.
This capability is a significant shift from traditional batch processing, where data is collected over a period and processed at intervals. Real-time analytics allows businesses and organizations to react to events and trends immediately, offering a significant competitive advantage.
Driving Business Agility and Responsive Decision-Making
Real-time analytics empowers organizations to be more agile and responsive. In dynamic market environments, the ability to make quick, informed decisions based on current data is invaluable. Real-time insights can lead to more effective strategies, from adjusting marketing campaigns on the fly to optimizing supply chain operations in response to current demand.
Future Outlook
As technology continues to advance, the scope and capabilities of real-time analytics are expected to grow. Innovations in AI and ML, edge computing, and IoT will further enhance the effectiveness of real-time data processing.
The future of real-time analytics promises not only faster insights but also more intelligent and predictive capabilities, driving further transformation across new sectors like telecommunications, logistics, and the public sector.
Challenges and Considerations
While the big data industry is enjoying multiple trends that will drive further growth, it also faces a range of challenges and considerations.
How these challenges will be dealt with moving forward, will have a defining impact on the how the trends above continue to develop.
Below are the biggest challenges the big data industry will tackle in the coming years.
Data Quality and Management
- Quality Concerns: Ensuring data quality is a significant challenge. Data collected from various sources can be inconsistent, incomplete, or inaccurate. Poor data quality can lead to incorrect conclusions and faulty business decisions.
- Management Complexity: Managing the sheer volume, variety, and velocity of big data is another daunting task. Organizing vast datasets, ensuring they are easily accessible and usable, and maintaining their integrity over time requires sophisticated data management systems and strategies.
Big Data Bias
- Bias in Data and Algorithms: Big data and AI algorithms can inadvertently perpetuate biases if the data fed into them is biased. This can lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes, especially in sensitive areas like hiring practices or loan approvals.
Technological Limitations and Infrastructure
- Scaling Challenges: As data volume grows, scaling existing data infrastructure to keep pace with this growth is a challenge for many organizations.
- Integration Issues: Integrating new big data technologies with existing IT infrastructures and workflows can be complex, resource-intensive, and expensive.
Regulations and Compliance Requirements
- Navigating Regulatory Landscapes: The legal landscape around data protection and privacy is rapidly evolving. Organizations must stay informed and compliant with various regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and others, which can vary significantly across regions.
- Compliance Costs and Complexity: Compliance with these regulations often requires significant investment in technology, processes, and training. Keeping up with changing regulations adds to the complexity and cost.
Conclusion
It’s clear that big data is a critical driver of innovation and strategic decision-making across various sectors. The integration of advanced technologies like AI and ML, the implementation of data fabric, the emergence of edge computing, and the growing importance of real-time analytics demonstrate the exciting capabilities of big data in transforming business operations and outcomes.
However, these advancements also come with inherent challenges.
Issues related to data quality, ethical data use, technological limitations, and stringent regulatory environments underscore the complexity of effectively leveraging big data. Navigating these challenges requires a strategic approach, balancing innovation with responsibility and ethical considerations.
As the big data industry continues to evolve, the future points towards even greater integration of data analytics in business and societal contexts.
Organizations that can successfully manage these trends, while addressing the challenges discussed above and adhere to regulatory standards, will be well-positioned to harness the full potential of big data in the future.
Disclosure/Disclaimer:
We are not brokers, investment, or financial advisers; you should not rely on the information herein as investment advice. If you are seeking personalized investment advice, please contact a qualified and registered broker, investment adviser, or financial adviser. You should not make any investment decisions based on our communications. Our stock profiles are intended to highlight certain companies for YOUR further investigation; they are NOT recommendations. The securities issued by the companies we profile should be considered high risk and, if you do invest, you may lose your entire investment. Please do your own research before investing, including reading the companies’ public filings, press releases, and risk disclosures. The company provided information in this profile, extracted from public filings, company websites, and other publicly available sources. We believe the sources and information are accurate and reliable but we cannot guarantee it. The commentary and opinions in this article are our own, so please do your own research.
Copyright © 2023 Edge Investments, All rights reserved.
