As our digital landscape takes flight into new and innovative transformations and possibilities, investors welcome the world of edge and cloud computing.
Picture a universe where data doesn’t just reside in distant servers but dances at the very edge of creation, where every command is met with instant response and where the ordinary transforms into the extraordinary.
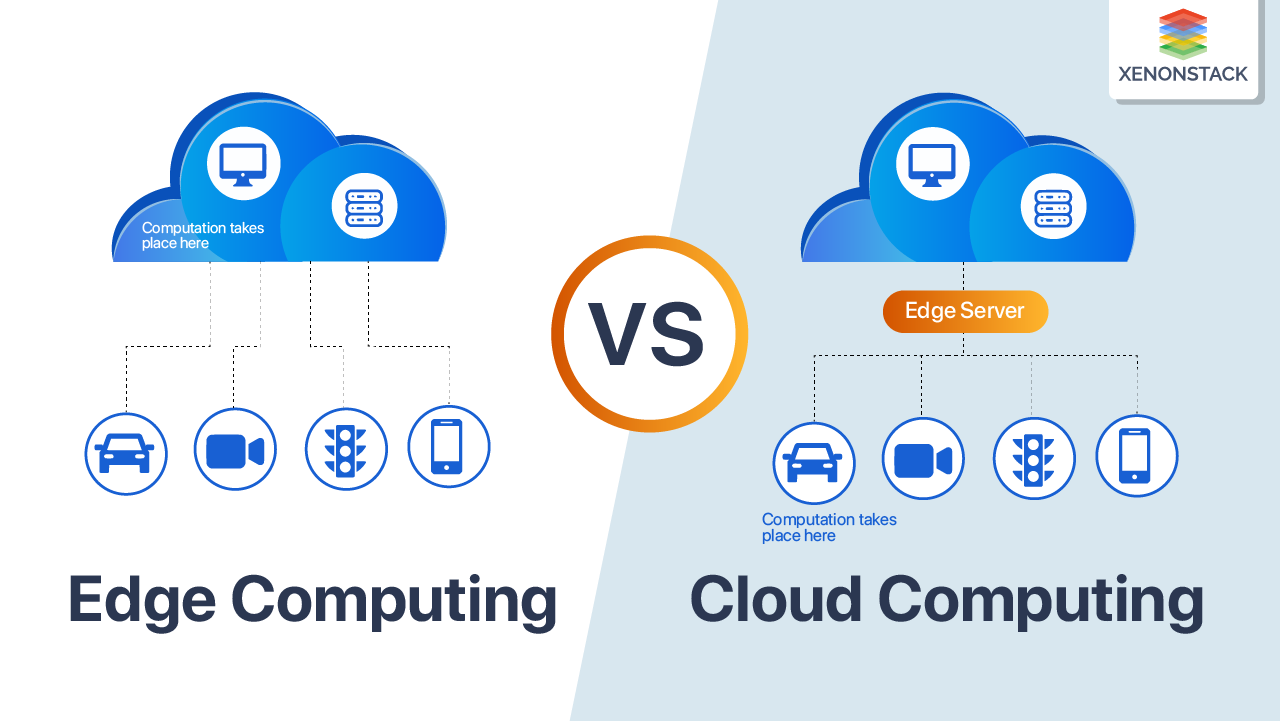
Edge computing vs cloud computing | XenonStack
Whether processing through remote servers or laboring at the edge, these two processes are at the forefront of computing power.
Journey with us as we discover the key differences between edge computing and cloud computing.
Key Aspects of Edge Computing
Picture your cellphone with a little helper wizard inside it, like a mini wizard apprentice (the front edge device). This mini wizard can do some thinking on your phone without constantly running to the big wizard tower (the cloud). So, when you ask your phone to do something, the mini wizard can quickly do it without waiting for the big wizard tower to respond.

Key Points | Adobe Stock
Edge computing transforms the paradigm in computing. It introduces a decentralized approach to data processing.
At its core, edge computing involves executing computational tasks closer to the source of data generation, often right at the “edge” of the network or, in our example, right inside your cellular device.
This proximity significantly reduces latency, enabling quicker response times and real-time decision-making.
Critical aspects of edge computing include its application in scenarios demanding low latency and high responsiveness, such as IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, and industrial processes.
By processing data locally, edge computing addresses the limitations of centralized cloud computing, particularly in environments where immediate actions are crucial.
Key Aspects of Cloud Computing
Investopedia says, “Cloud computing is the delivery of different services through the Internet.”
Many people use Apple products daily, and their “iCloud” is a perfect example of cloud computing.
Imagine iCloud as a magical cloud kingdom where you store photos, music, documents, and more.
When you take a photo on your iPhone, it’s saved in iCloud. Instead of keeping all your images on your iPhone, they float to the iCloud kingdom. If you lose your phone or get a new one, your photos are safe in the cloud, and you can easily access them with an internet connection.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cloud-computing-4199287-f346729f8f574000a3058b9ad69e9a41.png)
Cloud Computing | Investopedia
Here’s the cool part: iCloud isn’t just cloud storage; it’s like having a team of magical helpers. Let’s say you take a new photo on your iPhone. Instead of your phone doing all the work to ensure it’s saved and backed up, it sends a messenger to iCloud. The iCloud wizards take care of storing your photo, making sure it’s safe and sound.
In a nutshell, iCloud is like one of those remote data centers where your stuff lives and it’s also a team of helpers that ensure your things are safe and backed up. That’s a bit like how cloud computing works— A kingdom in the sky that is used to process data through a centralized data center!
Cloud computing is a cornerstone of modern IT infrastructure, characterized by its centralized data storage, processing, and service delivery model.
Critical aspects of cloud computing encompass its ability to offer on-demand access to a vast array of computing resources, from virtual machines to storage and applications, all delivered over the internet.
This scalability ensures flexibility, allowing businesses to scale up or down based on their needs.
Its shared resource model fosters collaboration and accessibility, enabling users to access applications and data from virtually any device with internet connectivity. With a focus on efficiency, reliability, and the offloading of computational complexities, cloud computing has become integral to diverse sectors, revolutionizing how organizations approach IT solutions and accelerating innovation on a global scale.
If you’d like to learn more about investing in cloud computing, click here.
Edge and Cloud Computing
Edge computing and cloud computing are both computing paradigms but differ in their approach to processing and managing data. Here’s a concise breakdown of the key differences:
Location of Processing data
- Edge Computing: Processing is done closer to the source of data generation, typically at or near the device or “edge” of the network. This reduces latency and enables quicker response times.
- Cloud Computing: Processing occurs in centralized data centers, often far from the end-users. This approach is efficient for tasks that don’t require immediate responses.
Data Processing Guide | Sprintzeal
Latency
- Edge Computing: Offers low latency as data processing happens locally, leading to faster response times. This is crucial for applications that demand real-time interactions, such as gaming or autonomous vehicles.
- Cloud Computing: Involves higher latency due to the distance between the user and the centralized cloud server. While suitable for many applications, it may not be optimal for time-sensitive tasks.
What Is Latency? | Design Gateway
Data Volume and Bandwidth
- Edge Computing: Ideal for processing a smaller volume of data locally, reducing the need for extensive bandwidth. It’s well-suited for applications where only relevant data needs to be sent to the cloud.
- Cloud Computing: Suited for handling large volumes of data and complex computations. It requires robust bandwidth for transmitting data to and from the centralized data centers.
Resource Scalability
- Edge Computing: Limited by the resources available at the edge devices. The capacity of individual edge nodes may constrain scalability.
- Cloud Computing: Offers virtually limitless scalability due to the extensive resources available in centralized data centers. It can handle growing workloads more efficiently.

Why Scalability is Important for Business on the Cloud | WHOA
Security and Privacy
- Edge Computing: This can enhance privacy by processing sensitive data locally without transmitting it to the cloud. Security measures are distributed across the network.
- Cloud Computing: Requires trust in the security measures the cloud service provider implements. Data is transmitted to centralized servers, raising privacy concerns in some cases.
While edge and cloud computing play crucial roles in the modern computing landscape, they cater to different use cases based on factors like latency, data volume, and the need for real-time processing.
When to use edge and cloud data processing
The choice between cloud computing and edge computing depends on specific use cases, requirements, and the nature of the application. Here are scenarios where each computing paradigm shines:
When to use Cloud Computing
Here are some areas where cloud services outperform edge computing:
How to Make the Best use of Cloud Services? | File Cloud
Flexibility
Cloud computing is ideal when you can quickly scale resources up or down based on demand. It’s highly flexible and suits applications with variable workloads.

Cloud Scalability and Flexibility Advantages for Business | Solution Dots
Extensive Data Processing and Storage
Cloud computing provides the necessary infrastructure and resources for applications involving large-scale data processing, complex computations, or extensive storage needs.
Accessibility and Collaboration
Suppose your application requires users to access data and applications from different locations or devices. In that case, a cloud computing service provider offers a centralized platform accessible over the internet, promoting collaboration and ease of use.

Accessibility | Medium
Cost-Effectiveness for Variable Workloads
Cloud computing allows you to pay for the resources you use, making it cost-effective for applications with variable workloads that don’t require constant, high-level processing.

Cost-Effectiveness Analysis | CDC
Global Reach and Availability
When your application needs to serve a global audience, cloud computing provides data centers in remote locations in various regions, ensuring low latency access and high availability for users worldwide.

Global Reach | The Content Craft
When To Use Edge Computing
Here are some examples of when edge computing is best used:
Low Latency and Real-Time Processing
Edge computing is optimal for applications that demand minimal latency and real-time processing, such as autonomous vehicles and specific industrial automation processes.
Low Latency | Reply
Bandwidth Constraints
In scenarios where bandwidth to a centralized computing system is limited or costly, edge computing can alleviate the strain by processing data locally, reducing the need to send large volumes of data to centralized cloud servers.
Enhanced Privacy and Security
For applications dealing with sensitive data, edge computing allows processing to occur locally, enhancing privacy and security by minimizing the transmission of critical information over networks.

Privacy | Forbes
Intermittent Connectivity
In environments with intermittent or unreliable connectivity to the cloud, edge computing ensures that applications can continue to function autonomously even when disconnected from centralized servers.

Connectivity | MIT News
Distributed Architecture
When the application architecture benefits from a distributed approach, with processing happening closer to where data is generated, edge computing provides a more efficient solution.
In many cases, a hybrid approach, combining elements of cloud and other edge computing systems (known as fog computing), may be the most suitable, allowing organizations to leverage the strengths of each paradigm based on specific requirements within a broader application ecosystem.
Which is Best?
The choice between edge and cloud computing isn’t a matter of being inherently better than the other; instead, it hinges on the specific requirements of the task. It’s akin to asking if a hammer is better than a screwdriver—they serve different purposes, and the efficacy depends on the job.

Which One Is Best | Boost Your Designs
Cloud computing excels in scenarios where scalability, centralized data processing, and accessibility are paramount. It’s the go-to for applications with fluctuating workloads, extensive data processing needs, and global accessibility requirements. The same cloud infrastructure is the backbone of many modern digital services, offering a centralized storage, computation, and collaboration hub.
Conversely, edge computing is spotlighted when low latency, real-time processing, and autonomy are critical. Applications like IoT devices and autonomous vehicles benefit immensely from processing data closer to the source. Edge computing shines in scenarios where immediate actions and reduced reliance on distant servers are essential.
Often, the optimal solution lies in a blend of both—fog computing—leveraging the strengths of edge and cloud computing within a cohesive architecture. This hybrid approach enables organizations to design systems that seamlessly balance the need for real-time responsiveness and the advantages of centralized resources.

Solutions | MaxPeople
In essence, it’s not about declaring one superior to the other but understanding the nuances and intricacies of each computing paradigm and strategically applying them based on the demands of the task or application. It’s a dance between centralization and decentralization, global reach and local immediacy, where the solution’s effectiveness is intricately tied to the unique requirements of the digital landscape at hand.
How to Invest in Edge and Cloud Computing
Investing in edge and cloud computing involves strategic considerations and a refined approach. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you navigate the investment landscape for these transformative technologies:
Research Both Paradigms
Gain a solid understanding of edge and cloud computing. Know their strengths, weaknesses, and the industries they impact.

How to measure research impact | Author Services
Consider a Hybrid Approach
Given the synergies between edge and cloud computing (fog computing), diversify your investments to include companies that leverage both paradigms.
Identify Key Players
Look for companies actively involved in edge computing. This includes firms providing hardware, software solutions, networking equipment, and services related to edge computing infrastructure.
Follow Industry News
Keep yourself updated on the latest developments in the edge and cloud computing industry. Subscribe to industry publications, follow reputable tech news outlets, and attend relevant conferences.

News | The Manufacturer
Explore Company Filings
Examine official filings and reports of companies you’re interested in. Publicly traded companies are required to submit regular reports to regulatory authorities. Check the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) website or equivalent regulatory bodies. If you’d like to learn more about analyzing stocks using annual reports and company filings, check out our post!
Leverage Financial Tools
Use stock screeners from financial websites or brokerage platforms. Filter stocks based on criteria like industry sector, market capitalization, or financial metrics. Focus on technology or IT sector stocks involved in edge and cloud computing.
Consider Technological ETFs
Look into exchange-traded funds (ETFs) or mutual funds focused on technology or disruptive innovations. Some funds specifically target companies in edge and cloud computing.

Technology ETFs | Investing News
Participate in Industry Events
Attend or follow conferences and events related to edge and cloud computing. These gatherings often showcase key players and emerging companies in the field.
Check Major Stock Exchanges
Investigate stock exchanges like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) or Nasdaq, where many technology companies are listed. Look for companies with a focus on edge and other cloud computing solutions.

Stock exchange | Britannica Money
Continuous Monitoring
The tech landscape evolves rapidly. Regularly reassess your investment strategy, staying informed about technological advancements and changes in market conditions.
Companies making advancements in Edge and Cloud Computing services
- Dell Technologies (DELL): Dell has been involved in delivering edge computing solutions, including hardware and software components designed for decentralized processing.
 Dell | Wikipedia
Dell | Wikipedia - NVIDIA (NVDA): Known for its graphics processing units (GPUs), NVIDIA has made strides in edge computing by providing powerful hardware for AI and high-performance computing at the edge.
 Nvidia | Nvidia
Nvidia | Nvidia - Intel Corporation (INTC): Intel is a significant player in providing processors and technologies that enable edge computing capabilities, especially in IoT and industrial applications.

Intel | Facebook
Cloud Computing:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) (AMZN): A dominant force in cloud computing, AWS continually introduces new services and features, shaping the cloud landscape. Amazon EC2, S3, and AWS Lambda are well-known offerings.
 Amazon Web Services Review | PCMag
Amazon Web Services Review | PCMag - Microsoft Azure (MSFT): Microsoft’s cloud platform, Azure, offers a comprehensive suite of services for computing, analytics, storage, and AI. Azure continues to expand its capabilities across various industries.
 Microsoft Azure | Teleco
Microsoft Azure | Teleco - Google Cloud Platform (GCP) (GOOG): GCP is Google’s cloud computing platform, providing a range of services, including computing, storage, and machine learning. Google’s expertise in AI and data analytics is reflected in offerings like BigQuery.
 Google Cloud Platform | Robot Wealth
Google Cloud Platform | Robot Wealth
Remember that the landscape is dynamic, and new entrants or shifts in market dynamics may have occurred. It’s advisable to check these companies’ latest developments and financial reports for the most up-to-date information.
Key Takeaways
In a recent article with Forbes, Ron Martino, Vice President for NXP Semiconductors, said, “We’re entering a new age of compute. We may not see the edge, but we will surely experience a dramatically different world of compute ushering in new experiences and economic models.”
As our digital landscape propels itself into new frontiers of innovation, investors find themselves at the crossroads of edge and cloud computing. Embarking on a journey to unravel the distinctions between edge and cloud computing helps to discover the magic woven into each paradigm.

Digital Technology Landscape | Goldhill Group
With its mini-wizard approach, Edge computing brings computation closer to the source, reducing latency and ushering in real-time decision-making—perfect for scenarios demanding swift responses, like IoT devices or autonomous vehicles.
Meanwhile, the enchanted iCloud kingdom exemplifies cloud computing, which operates with centralized efficiency, offering scalability, flexibility, and accessibility on a grand scale with solely an internet connection. If you’d like to learn more about the future of the internet, check out our video on Web 3.0!
In this dance between edge and cloud, there is no supremacy; instead, there is a delicate interplay of strengths. A subtle understanding leads to the realization that each paradigm serves a unique purpose, much like the choice between a hammer and a screwdriver. Cloud computing excels in scalability, extensive data, and processing power, while edge computing shines in low latency and real-time scenarios.
Investing in these transformative technologies requires a thoughtful approach. Understanding edge and cloud computing, diversifying portfolios, researching key players, and staying informed are essential steps. A hybrid investment strategy that appreciates the synergy between the two paradigms ensures resilience in a dynamic market landscape.
While investors like yourself continuously expand their horizons and education, understanding the distinctions of fluidity, adaptability, and effectiveness within computational resources will bring you closer to financial freedom.
In the grand spectacle of technology, edge and cloud computing share the spotlight, contributing their distinct brilliance to the ever-evolving performance of the digital age.
Disclosure/Disclaimer:
We are not brokers, investment, or financial advisers; you should not rely on the information herein as investment advice. If you are seeking personalized investment advice, please contact a qualified and registered broker, investment adviser, or financial adviser. You should not make any investment decisions based on our communications. Our stock profiles are intended to highlight certain companies for YOUR further investigation; they are NOT recommendations. The securities issued by the companies we profile should be considered high risk and, if you do invest, you may lose your entire investment. Please do your own research before investing, including reading the companies’ public filings, press releases, and risk disclosures. The company provided information in this profile, extracted from public filings, company websites, and other publicly available sources. We believe the sources and information are accurate and reliable but we cannot guarantee it. The commentary and opinions in this article are our own, so please do your own research.
Copyright © 2023 Edge Investments, All rights reserved.
