In 2020, the world was rocked by the COVID-19 pandemic, which shut down the world as we know it. However, as you know, money never sleeps, and people needed to figure out a way to keep working away from the office.
As such, digital solutions became entrenched in workplace culture. Despite the economic turmoil of 2023, cloud computing services continue to surge ahead in growth.
What are cloud computing services?
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services (servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, etc.) over the internet, non-reliant on physical location(s). The organizations that provide and manage these tools are referred to (creatively) as cloud computing providers.
With that being said, I will guide you through this sector by exploring the following:
- Why a business would invest in the technology
- The types of cloud computing businesses
- Why you should invest in the sector
- What the market looks like
- What stocks to take a look at
Why would a business invest in the technology?
The technology offers unique advantages for businesses:
- Flexibility and cost cutting, as businesses no longer need to buy and manage hardware and software. Services are accessed on demand, when and where they are needed.
- The remote servers allow for the outsourcing of key company functions like data backup, network management, and business continuity contingency planning.
- Businesses can use large amounts of processing power when they need it to host applications that may require said power.
- If you are a company in the industry, it lets you offer your software on a subscription or pay-per-use model, which means your TAM is massive.

Image by: Cyberian Technologies
There are some stated drawbacks of the technology, these include:
- Cloud-based solutions require a quick and reliable internet connection. Now, this is common in metropolitan centers, but rural areas may not have the connection required. If you are one of the more savvy investors (which I am sure you are), you will take a peek at how 5G technologies are closing this gap and what it means for the sector.
- Security and privacy are key concerns in cloud computing. Businesses that utilize both public and private clouds (hybrid clouds) have to be extra vigilant and invest extra resources to maintain the integrity of the data, in terms of access control. In addition, if there is a security breach of a cloud-based solution provider, it could risk the data of multiple companies and users.
- There is a high cost of change involved when a business decides to migrate to the cloud. There must be skilled employees to facilitate the migration, and there are associated costs for rewriting applications.
Types of cloud computing companies
Typically, these services and the adjacent cloud infrastructure come in identifiable sub-sectors.
Image by: Electronics 360
For your ease, I will segment them. This is not an exhaustive list, but it is a handy way to delineate the most common ones:
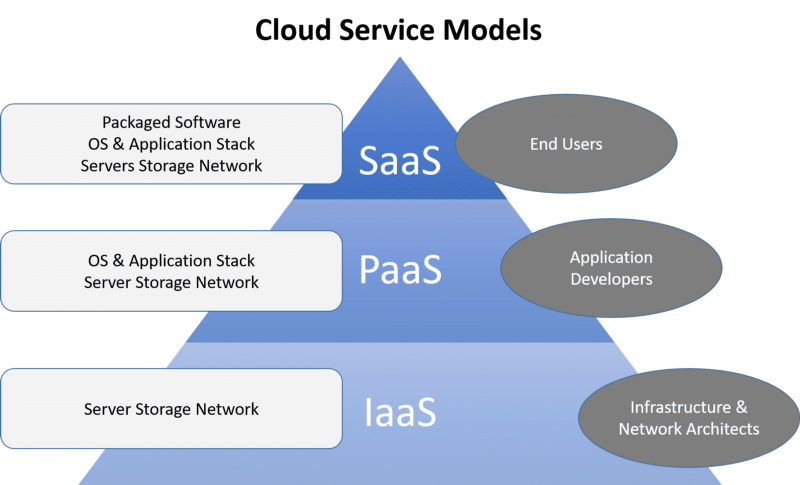
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS Companies): Provides virtualized computing resources where users have control over the O/S, configuration, application, etc. At the same time, the cloud computing provider manages the actual physical infrastructure.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS Companies): Offers the platform and environment for the development, testing, and deployment of applications. The infrastructure is pre-configured (including the O/S, development tools, and database management systems). A developer can thus just worry about application development.
 Image by: Spiceworks
Image by: Spiceworks - Software as a Service (SaaS Companies): The most commonly understood of cloud technology companies, SaaS, is involved in the delivery of software applications over the internet, often on a subscription basis. Usually, access to the software is done via a web browser or a thin client (no, I am not talking about a new diet regime) without needing installation or maintenance.
- Database as a Service (DBaaS Companies): DBaaS is involved in the management of data storage and database services. The cloud provider handles database administration tasks while users store and access data in a scalable and secure way without having to manage the underlying mechanisms of the cloud-based solution.
Why invest in cloud computing & cloud technology?
Let’s talk investing in the cloud computing sector as an investment theme.
Investors always look to innovative and emerging industries for above-normal returns. Such an investing strategy lends itself to the cloud computing sector, being a sector chock full of exciting companies.
We are seeing numerous businesses moving towards cloud-based software and cloud-based applications. In fact, this movement has been key for small companies and large organizations alike to stay competitive with their respective market(s).
From an operational standpoint, cloud technology lets workers at these companies access proprietary systems, platforms, and files as remote working continues to grow.
Even more reasons to invest in the cloud
Need more reasons to start investing in cloud computing stocks? Well, how about these:
- Cloud computing is expected to grow by +$287 billion from 2020-2025
- Growth has been strong, and there is still a massive runway for growth as more and more businesses move to cloud solutions
- New business models have been made possible by the advancement of cloud computing technology (SaaS, IaaS, CaaS, etc.)
- 69% of organizations have accelerated their migration to cloud services and cloud infrastructure
- By the end of 2025, about 49% of company data will be stored on the public cloud
- Platform as a Service (PaaS) is the most rapidly growing sub-sector
The Cloud Services Market
By the end of this decade, the spend on global cloud computing will be at around $1 trillion, meaning cloud companies are somewhere investors should be looking to.
The market is dominated by a few familiar players that are often at the forefront of innovation (much like what we are seeing with artificial intelligence).
Amazon Web Services enjoys 32% of the market share, Microsoft Azure comes in second with the 23%. The Google Cloud has 10% of the market, and finally, the Alibaba cloud accounts for 4% of the market.
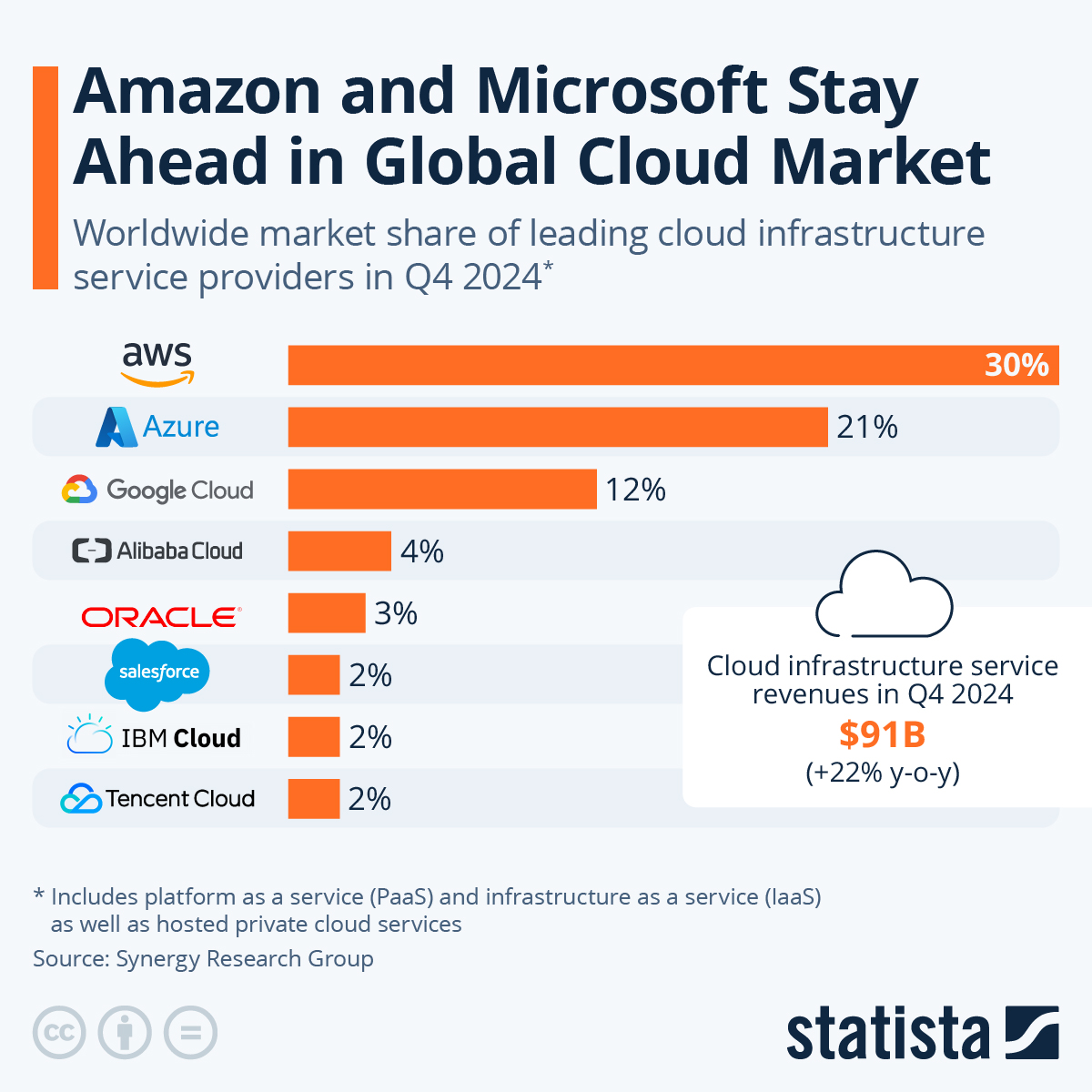
Image by: Statista
The largest cloud providers usually compete in a mix of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, while smaller providers usually operate on one level of cloud service solutions.
The IaaS sub-sector
The IaaS sector is a massive sub-sector dominated by three massive players in cloud computing.
Amazon Web Services, the largest cloud technology company, utilizes their Elastic Compute Cloud product. Clients have the ability to run and end applications on virtual machines, as they need.
Microsoft Azure has a wide range of solutions across multiple functions. Their IaaS offering allows organizations to access remote servers. Clients can then develop their own software or run third party applications.
The Google Cloud platform is also multi-functional. Their IaaS offering is called the Google Compute Engine (GCE), and it allows clients to run their virtual infrastructure on the same infrastructure Google uses to run its search engine, YouTube, their Google App Engine, etc.
The PaaS sub-sector
The PaaS sub-sector is like the IaaS with the extension that allows customers to develop and distribute their own applications on said platform. Allowing the company to invest in the development without needing to invest in the hardware.
The usual players dominate this industry (Microsoft, Amazon, Alphabet). However, other players have been able to penetrate the market. SAP, Salesforce, Twilio, and IBM have made industry leading PaaS offerings, that are widely used.
The SaaS sub-sector
SaaS organizations dominate the cloud services industry, (on track to be worth $197 billion in 2023), allowing customers to access software on a pay-per-use or subscription basis.
There is an incredible amount of SaaS companies with household names like Microsoft Office 365, Netflix, Zoom, etc.
Confusingly, SaaS businesses and products can be built on the back of PaaS products, which are de-facto extensions of IaaS products. Understand? Good.
Cloud Stocks
True and tried…
The safest bet to get into the sector lies with investing in the three large giants:
- Amazon (AWS)
- Microsoft (Azure)
- Alphabet (Google cloud)
These are not pure play cloud organizations, but offer serious exposure to the exploding industry while being backed by legacy business models and products. They also enjoy the most comprehensive software and partnerships ecosystem with third party SaaS providers.
A little more exciting…
Now, like many investors that love growth opportunities, you want to seek out more cloud exclusive plays, there are a few cloud stocks that one may consider.
Salesforce ($CRM)
This company is a stalwart in the CRM sub-industry since the late 1990s. Via acquisitions and organic growth, the organization has been able to branch out to different areas and innovate at a rate consistent with the market.
Investors can achieve their growth-oriented investment objectives using the Salesforce stock, as the company invests in and acquires stakes in smaller cloud computing players (Snowflake, Monday.com, etc.).
The company is extremely profitable and is poised to become one of the biggest tech companies in the next decade.
Some key stats include:
- TTM Revenue = $33.07 billion
- Revenue 5-Year Growth = 24.41%
- TTM EPS = $1.59
- EPS 5-Year Growth = -15.70%
- TTM Operating Cash Flow = $8.40 billion
Unity Software ($U)
Unity Software helps video game developers transition to the world of cloud computing. The company is an innovative 3D content creation platform, seeing millions of users utilize all its offerings.
Aside from video game developers, companies like Volkswagen and Toyota utilize the offerings for auto design creation.
As well, Unity allows content creators freedom and autonomy over the entire phase of creation and go-to-market strategy, all in real time.
Some key data includes:
- TTM Revenue = $1.81 billion
- Revenue 5-Year Growth = 38.47%
- TTM EPS = -$2.86
- EPS 5-Year Growth = -56.59%
- TTM Operating Cash Flow = -$75.32 million
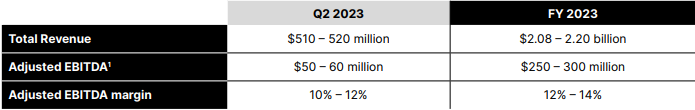
Trade Desk Inc. ($TTD)
The Trade Desk is a generally new powerhouse in the emerging world of programmatic advertising, ranking as the largest independent digital advertising management software company.
Digital advertising is poised to continue to grow and penetrate new use cases like in-home on demand entertainment for both TV and movies.
This is for someone interested in investing in cloud computing and the future it has, a growth-oriented investor.
Some key stats include:
- TTM Revenue = $1.73 billion
- Revenue 5-Year Growth = 38.96%
- TTM EPS = $0.26
- EPS 5-Year Growth = -1.47%
- TTM Operating Cash Flow = $626.44 million
WisdomTree Cloud Computing Fund ($WCLD)
Among the exchange-traded funds that are focused on cloud computing, this ETF stands above for those interested in ETF investing.
This passively managed ETF (as opposed to the plethora of actively managed ETFs) offers a low-cost, transparent, and flexible exposure to the sector.
The fund has compiled assets of just under $600 million (making it a relative giant among cloud computing ETFs) as it seeks to match and then outpace the BVP Emerging Cloud Index.
The ETF is weighted heavily in information technology (87.84%), with its top 10 holdings accounting for 17.72% of TAUM.
Some key data includes:
- Total Assets = $571.94 million
- NAV = $26.883
- Expense Ratio = 0.45%
- YTD Returns = 18.67%
To wrap this up
When we think of the sector, the words that come to mind are scalability, flexibility, and cost efficiency—painting a picture of an industry that is robust and poised for sustainable growth.
As someone interested in investing in the space, you must make sure to do all the necessary due diligence (like combing through a prospectus carefully) and make yourself familiar with the metrics of success of the sub-sector you wish to invest in.
As always, please do your own research as this does not constitute investment advice…just my own two cents on the cloud industry.
