As investors like you and I diversify our holdings to the new and unknown world of quantum technology, it opens up a unique chance for us to explore the fantastic abilities of the quantum computer.
In the contemporary investment landscape, the allure is found in the prospect of unravelling intricate problems that elude the grasp of conventional computing. According to Forbes, “Quantum computing technology will impact everything from cryptography to medicine to finance.”
The transformative prowess of quantum algorithms extends its reach into diverse sectors, spanning finance to even the intricate realms of drug discovery.
Quantum Computing | Shuttershock
Yet, with immense promise comes inherent risks, as practical and scalable quantum computers are still in their early stages. Navigating this landscape demands a nuanced understanding of evolving technologies and a recognition of the experimental nature of quantum computing investments.
For those seeking financial returns and the excitement of cutting-edge innovation, investing in the quantum realm unveils a dynamic dance between possibility and uncertainty.
What is quantum computing?
Quantum computing is a revolutionary paradigm that harnesses the principles of quantum mechanics to process information. Unlike traditional classical computing methods that use bits to represent either a 0 or a 1, quantum computers use quantum bits or qubits.
Qubits can exist in multiple states simultaneously, a phenomenon known as superposition, enabling computers to perform complex computations at speeds exponentially faster than classical computers to solve complex problems.
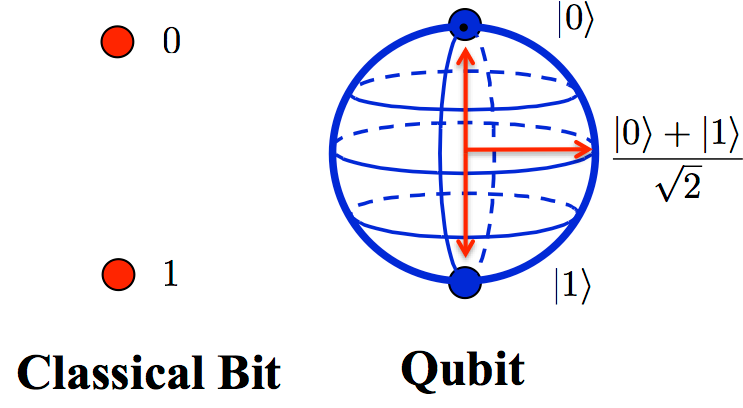
Qubit | Poetry In Physics
Moreover, quantum technology can leverage entanglement, a quantum phenomenon where one qubit’s state is dependent on another’s state, even when physically separated. This interconnectedness allows quantum computing technology to solve problems by considering multiple possibilities simultaneously.
Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize fields such as cryptography, optimization, and drug discovery, addressing problems that are practically impossible for classical computers. However, building practical and scalable quantum machines remains a significant technological challenge, and the field is still in its early stages of development.
Quantum Computers
Quantum computers are the physical devices or machines that implement quantum computing principles. These are the actual hardware systems designed to manipulate and process qubits. These machines aim to simulate quantum systems and perform computations exponentially faster than classical computers, particularly for problems like factoring large numbers, simulating quantum systems, or optimizing complex systems.
Computer | Medium
Quantum Computing Hardware
Quantum computing hardware refers to a quantum computer’s physical components and technologies. Unlike regular computers, their hardware is designed to manipulate and control qubits to perform quantum computations. Here are some key elements of quantum computing hardware:
Qubits
Qubits, or quantum bits, are the fundamental building blocks of quantum computing. They can exist in multiple states simultaneously (superposition) and can be entangled with each other, enabling quantum computers to process information in parallel.
Quantum Gates
Quantum gates are the equivalent of classical logic gates in quantum computing. They manipulate the quantum states of qubits to perform quantum operations. Common quantum gates include Hadamard gates, CNOT gates, and phase gates.
Superconducting Circuits
Many quantum computing projects use superconducting circuits, which are electrical circuits that can carry electric current without resistance when cooled to extremely low temperatures. Superconducting qubits are manipulated using microwave pulses.
Superconducting | Wikipedia
Ion Traps
Quantum computers based on ion trap technology use individual ions as qubits. These ions are manipulated and entangled using electromagnetic fields. Laser beams are often used to perform quantum operations on ion-trapped qubits.
Topological Qubits
Some quantum computing architectures aim to use topological qubits, which are believed to be more robust against errors. These qubits are based on anyons, exotic particles that exist in certain materials.
Cryogenic Systems
Quantum computers often operate at extremely low temperatures, near absolute zero, to maintain the delicate quantum states of the qubits. Cryogenic systems, including sophisticated refrigeration technology, are essential components of quantum computers.
Quantum Processors
Quantum processors are the core computational units of quantum computers. They consist of arrays of qubits, quantum gates, and the necessary control and readout mechanisms. The architecture varies among different quantum computing platforms.
Quantum Memory
Quantum memory is crucial for preserving the quantum states of qubits during computations. This is challenging due to the susceptibility of quantum states to decoherence or loss of coherence.

Quantum Memory | Forbes
Control Electronics
Control electronics include systems that apply external signals, such as microwave pulses or laser beams, to manipulate and control the qubits. These systems are responsible for executing algorithms.
Quantum computing hardware is an evolving and interdisciplinary field that involves expertise in quantum physics, materials science, cryogenics, and electronics. Researchers and engineers continue to explore different approaches and technologies to build scalable and fault-tolerant quantum computers.
As investors, it is crucial to understand the companies and industries you choose to invest in. Even with the short description of the main aspects of quantum computers above, it is essential to know where your circle of knowledge begins and ends and whether or not it is suitable for you to invest in a given industry.
Why invest in quantum computing?
Investing in quantum computing presents a unique opportunity for several reasons:
Potential for Revolutionary Breakthroughs
Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize various industries by solving complex problems exponentially faster than classical computers. This includes cryptography, optimization, drug discovery, materials science, and artificial intelligence applications.
Competitive Advantage
Companies and investors involved in quantum computing development and research may gain a competitive edge in technological innovation. Being at the forefront of this transformative technology can position organizations for future growth and leadership.
Competitive Advantage | Market Maven
Disruption of Existing Technologies
Quantum computing has the potential to disrupt existing technologies and industries. Investing early in this field allows individuals and organizations to adapt to and capitalize on these disruptions rather than being left behind.
Emerging Quantum Ecosystem
As the quantum computing field advances, an ecosystem of companies, startups, and research institutions is emerging. Investing in this ecosystem provides exposure to various opportunities, from hardware development to developing quantum computers’ software and applications.
Government and Corporate Investments
Many governments and major technology companies are making substantial investments in quantum research. Investing in quantum research in alignment with these trends may offer opportunities to participate in collaborative efforts and benefit from industry-wide advancements in developing quantum technology.

Government Spending | Fraser Institute
Long-Term Investment Potential
Quantum computing is still in its early stages, and hardware, algorithms, and error correction breakthroughs are ongoing. Long-term investors may see the potential for significant returns as the technology matures and becomes more widely adopted.
Diverse Applications
Quantum computing is not limited to a specific industry; its applications span multiple sectors. This diversity increases the range of potential opportunities and reduces dependence on the success of a particular application.
Intellectual Property Portfolio
Investopedia defines intellectual property as “Intangibles owned and legally protected by a company from outside use.”
Companies engaged in quantum computing often build valuable intellectual property portfolios. Investing in businesses with solid patent positions in their quantum computer technologies may provide strategic advantages.

Intellectual Property | Investopedia
It’s essential to note that quantum computing is a high-risk, high-reward area. Challenges such as maintaining quantum coherence (error correction), scaling qubit count, and addressing environmental factors require ongoing research.
Potential investors should carefully assess their risk tolerance, stay informed about technological developments, and consider diversifying their investments to mitigate risks associated with the developing nature of the quantum computing market.
Additionally, consulting with financial advisors knowledgeable about technology can provide valuable insights for making informed investment decisions.
How to Invest in Quantum Computing
Investing in quantum computing involves understanding the current landscape of the quantum computing sphere, identifying investment opportunities, and considering the risks associated with this emerging technology. Here are steps to guide your investment approach:
Educate Yourself
Gain a solid understanding of quantum computing technology, its principles, and potential applications. Stay informed about the latest developments, breakthroughs, and challenges in the field.

Education | Adobe Stock
Research Companies
Identify companies actively involved in quantum computing research and development. This includes established tech giants, startups, and companies focusing on quantum computing developments in hardware, software, or applications. Some notable players include IBM, Google, and Microsoft.
Diversify Investments
Diversify your investments across various aspects of the quantum computing ecosystem. Consider allocating funds to companies involved in quantum hardware and development, quantum software, and applications in finance, healthcare, and materials science industries.
Diversification | Investopedia
ETFs and Mutual Funds
Quantum computing ETFs are perfect for investors looking to join the global technology industry. Look for exchange-traded funds (ETFs) or mutual funds focusing on technology, innovation, or disruptive technologies. Some funds specifically target quantum computing or related technologies, providing a diversified approach to investing in the sector. If you are interested in new opportunities involving ETFs, check out our post on Bitcoin’s exchange-traded fund.
Consider Research and Patent Positions
Examine companies’ research efforts and patent positions in quantum computing. Strong intellectual property portfolios may indicate a company’s leadership and potential for future growth.
Evaluate Partnerships and Collaborations
Companies engaged in strategic partnerships with major technology firms, research institutions, or government entities may have a more collaborative and supportive environment, which can positively impact their potential for success.
Stay Informed about IPOs and Funding Rounds
Monitor initial public offerings (IPOs) and funding rounds of companies in the quantum computing space. These events can provide investment opportunities and insights into the market’s confidence in specific companies.

IPO | Investopedia
Click here for a comprehensive list of pre-IPO tech companies!
Assess Financial Health
Evaluate the financial health of companies you’re considering for investment. Consider factors such as revenue growth, cash flow, and the company’s ability to navigate challenges and execute its business strategy.
Financial Health | Utah State University
Understand Risks
Recognize the inherent risks associated with investing in emerging technologies. Quantum computing is still in its early stages, and technological, regulatory, and market risks exist. Be prepared for the possibility of volatility and uncertainties.
Consult Financial Advisors
Seek advice from financial advisors who specialize in technology investments. They can provide insights into market trends and potential risks and help tailor your investment strategy to align with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Remember that investing in quantum computing carries risks, and it’s essential to conduct thorough due diligence. Consider the technology’s long-term potential, stay updated on industry developments, and make investment decisions based on a well-informed and diversified approach. If you want to read more about investing opportunities in quantum computing, click here!
Pros and cons of investing in quantum computing
Navigating the quantum computing landscape entails addressing regulatory and ethical considerations, particularly in domains like cryptography. Investors must consider potential regulatory challenges that may influence the industry’s trajectory.
In addition, the quantum computing industry’s early stages may contribute to market volatility, with investor sentiment and perceptions of technological progress influencing market dynamics. Given the limited availability of pure-play quantum computing companies for public investment, investors might explore diversification across related technologies or consider investments in companies engaged in either quantum computing exposure or research within more giant conglomerates.

Pros and Cons | Medium
Successful investment in the quantum computing sector demands a meticulous evaluation of associated risks and a long-term perspective. Staying up-to-date on technological advancements, industry shifts, and the evolving competitive landscape is crucial for investors as they assess risk tolerance and investment goals.
Quantum Computing Stocks to Add to Your Watchlist!
Here are some companies at the forefront of the quantum sector:
Lockheed and Martin (LMT)
Lockheed Martin is a global aerospace and defence company that is one of the world’s largest and most prominent defence contractors. Headquartered in Bethesda, Maryland, USA, Lockheed Martin is a leading provider of advanced technology systems, products, and services for various sectors, including defence, intelligence, space, and aeronautics.

Lockheed Martin | Lockheed Martin
The company plays a significant role in developing and manufacturing cutting-edge technologies used in military and civilian applications.
Intel (INTC)
Intel Corporation, commonly known as Intel, is a multinational technology company that is a global leader in the design and manufacturing of semiconductor chips and related technologies.
Founded in 1968, Intel has become one of the world’s largest and most influential semiconductor companies, playing a crucial role in the evolution of the computing industry.

Intel | Intel
Google (GOOG)
Google is a multinational technology company that specializes in Internet-related services and products. Founded in 1998 by Larry Page and Sergey Brin while they were Ph.D. students at Stanford University, Google has become one of the world’s most influential and dominant technology companies.

Google | Google
The company’s mission is to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.
Honeywell (HON)
Honeywell is a multinational conglomerate that operates in various industries, offering various products and services. Honeywell has been actively involved in the field of developing quantum computing hardware.

Honeywell | Honeywell
Honeywell Quantum Solutions is a division of Honeywell that focuses on advancing and commercializing quantum computing technologies. Quantum computing is an area that leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to perform calculations that would be challenging or impossible for classical computers.
IBM (IBM)
IBM, or International Business Machines Corporation, is a pioneering multinational technology and consulting company with a rich history dating back to 1911. Recognized for its diverse business operations, IBM engages in hardware, software, cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and consulting services.

IBM | IBM
Renowned for its mainframe computers, the company has become a key player in software development, cloud services, and emerging technologies like quantum computing. With a global presence, IBM is committed to innovation, research, and corporate social responsibility, shaping the landscape of the technology industry and offering a broad range of solutions to clients worldwide.
Understand Your Investment
In conclusion, investing in a quantum computing system presents a groundbreaking opportunity at the intersection of finance and revolutionary quantum mechanics.
Companies spearheading research and development in quantum computing, such as IBM, Google, Lockheed Martin, Intel, and Honeywell, are drawing investor interest with the promise of solving complex problems beyond the reach of classical computers. As the technology landscape continuously evolves, staying updated with new innovations in the tech realm is vital. Click here if you would like to learn more about the future of technology and the capabilities of the Web.
Quantum algorithms hold transformative potential across various industries, from finance to drug discovery, offering financial returns and cutting-edge innovation excitement. However, the developing nature of practical and scalable computers introduces inherent risks.
Navigating this dynamic landscape requires a nuanced understanding of evolving technologies, recognition of the experimental nature of quantum computing investments, and careful consideration of long-term potential amidst uncertainties.
As quantum computing advances, investors like you and I can readily explore the dynamic interplay between possibility and uncertainty.
Disclosure/Disclaimer:
We are not brokers, investment, or financial advisers; you should not rely on the information herein as investment advice. If you are seeking personalized investment advice, please contact a qualified and registered broker, investment adviser, or financial adviser. You should not make any investment decisions based on our communications. Our stock profiles are intended to highlight certain companies for YOUR further investigation; they are NOT recommendations. The securities issued by the companies we profile should be considered high risk and, if you do invest, you may lose your entire investment. Please do your own research before investing, including reading the companies’ public filings, press releases, and risk disclosures. The company provided information in this profile, extracted from public filings, company websites, and other publicly available sources. We believe the sources and information are accurate and reliable but we cannot guarantee it. The commentary and opinions in this article are our own, so please do your own research.
Copyright © 2023 Edge Investments, All rights reserved.
